In the complex architecture of 5G networks, the 5G Core (5GC) serves as the central hub, managing various network functions and enabling seamless connectivity. Among these functions, the Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) plays a pivotal role as a critical control plane function.
The AMF is responsible for terminating the control plane of different access networks onto the 5GC and determining which User Equipment (UE) can access the 5GC to exchange traffic with Data Networks (DNs), including the internet and other external networks.
The primary tasks of the AMF can be summarized as follows:
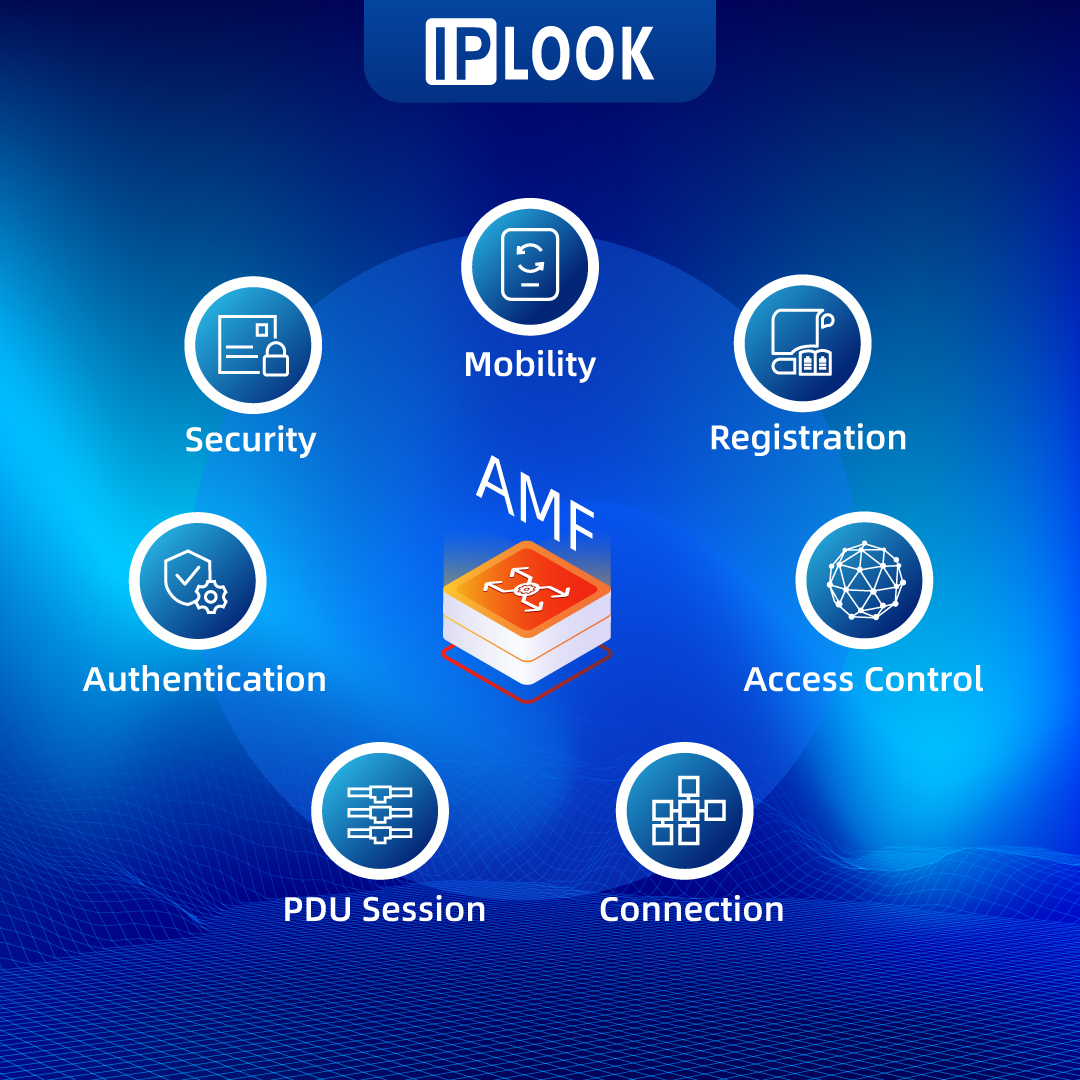
· Registration and Authorization: The AMF ensures secure and authorized access to the network by onboarding devices, verifying their credentials, and enforcing network access policies. This helps maintain network integrity and prevents unauthorized access.
· Access Control: The AMF governs access to the network based on predefined policies and user profiles, granting or restricting access as required. This ensures that network resources are utilized efficiently and that only authorized devices can exchange traffic.
· Mobility Management: One of the key responsibilities of the AMF is ensuring seamless connectivity for UEs in motion. As users move between different cell towers, the AMF facilitates handovers and maintains uninterrupted service, providing a consistent user experience.
· Connection Management: The AMF establishes, maintains, and releases connections between UEs and the 5GC, providing a stable communication path for data exchange. This helps maintain reliable connectivity and enables smooth communication within the network.
· PDU Session Handling: The AMF interacts with the Session Management Function (SMF) to set up, modify, and release data transfer sessions with other networks. This supports efficient session management and ensures seamless connectivity.
· Security Assurance: Lastly, the AMF plays a crucial role in maintaining network security by authenticating UEs, managing encryption keys, and implementing ciphering algorithms. This ensures that communication within the network remains secure and protected against potential threats.
In conclusion, the AMF is a vital component of the 5GC network, enabling secure, reliable, and seamless connectivity for UEs. Its various functions, from registration and authorization to mobility management and security, make it an indispensable part of the 5G Core network architecture.
To learn more about AMF and its role in empowering efficient network operations, click to explore IPLOOK's 5GC AMF.

