To meet the diverse billing requirements of EPC, 5GC and IMS, a converged charging architecture is introduced, offering online charging, offline charging, and converged charging for 4G/5G/IMS.
Online Charging: The user's account balance is monitored to determine if it is depleted or exceeds the available credit limit. In such cases, the system immediately suspends the service until the balance is replenished, at which point the service can be resumed.
Offline Charging: The account balance is updated within a specified time range, and the charging process does not have a real-time impact on the service. Instead, it follows a fixed schedule (daily/monthly/yearly) for settlement. If no renewal is made, the service is suspended on the settlement date.
With the evolution of various options of SA/NSA, different charging architectures have transformed from traditional offline charging and online charging to a converged charging system. A converged charging system combines online and offline charging of the 4G/5G core network, providing a centralized deployment and a unified service interface for managing detailed bills, including call records, messages, and value-added services.
By using a converged charging architecture, it is possible to comprehensively measure and manage user resource utilization, customize billing strategies, and provide complete itemized bills.
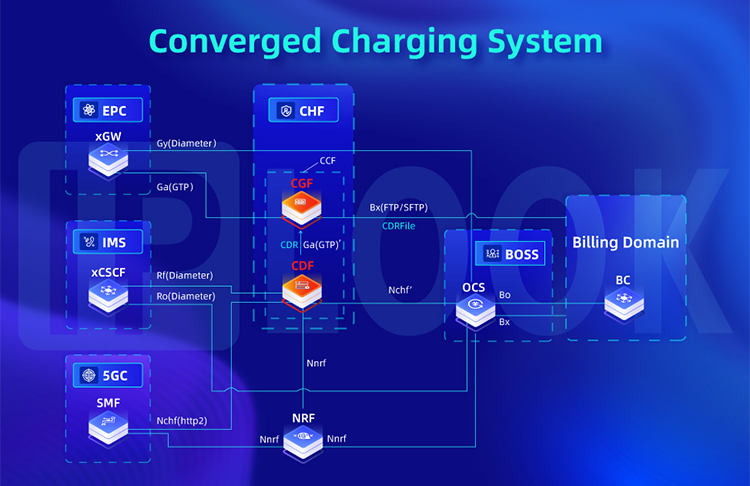
As shown in the diagram, the CHF implements the CDF (Charging Data Function) and CGF (Charging Gateway Function) functionalities internally. The CDF connects with IMS via the Rf interface, supporting offline charging. It also connects with 5GC via the Nchf interface, supporting converged charging and offline charging services. For offline charging, the CDF supports the initiation, update, and closure of CDRs (Charging Data Records) based on Rf/Nchf interface messages.
For online charging, the CDF supports forwarding Nchf interface messages to the OCS (Online Charging System) via the Nchf'/Gy interface, processing the billing response from the OCS, and forwarding it to the billing request endpoint. After generating CDRs, the CDF sends them to the CGF for further processing through internal interfaces.
The CGF connects with the EPC via the Ga interface to receive offline CDR data generated by the EPC. Additionally, the CGF connects with the CDF via internal interfaces to receive CDR data generated by the CDF. The CGF has functionalities for parsing and validating CDR data, according to 3GPP TS 32.297, to classify and assemble CDR files. The CGF sends the CDF files to BD (Billing Domain) through the Bi interface. Furthermore, the CGF should support BD-initiated requests for obtaining CDR files.
The converged charging architecture supports the conversion of received billing information into billing records, which can be stored locally or forwarded in real-time to the charging system. It is also compatible with both service-oriented interfaces and non-service-oriented interfaces to cater to diverse billing requirements.

