In the telecommunications industry, data transmission is a critical aspect, and there are two primary approaches to managing data flow: Grant-Free and Grant-Based systems. These systems differ in how they allocate resources for data transmission and each has its unique advantages and use cases. In this article, we'll briefly compare Grant-Free and Grant-Based systems.
Grant-Free Systems
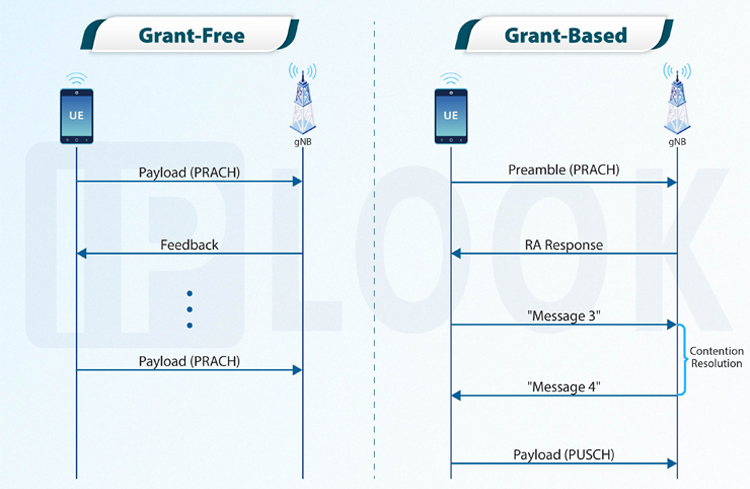
Grant-Free systems are designed for scenarios where data is transmitted sporadically or in short bursts. In these systems, resources for data transmission are allocated without prior grant or reservation. This approach is well-suited for low-latency applications and enables devices to transmit data quickly without having to wait for resource allocation. One of the main benefits of Grant-Free systems is their ability to support a large number of devices simultaneously, making them ideal for IoT applications. They also enable low-latency connectivity, as devices can transmit data immediately without waiting for a grant. However, Grant-Free systems may not be suitable for applications that require high throughput or sustained data transmission, as they can experience congestion and reduced performance in such scenarios.
The procedure of Grant-Free systems is as follows:
· Devices (UEs) generate data packets to be transmitted.
· Devices send the data packets using a Payload on the Physical Random Access Channel (PRACH).
· The network (Base Station, BS) receives the data packets and sends feedback to the devices.
Grant-Based Systems
Grant-Based systems are designed for scenarios where data is transmitted continuously or in large amounts. In these systems, resources for data transmission are allocated through a grant process, where devices request resources from the network before transmitting data. This approach ensures efficient use of resources and is well-suited for high-throughput applications.
The procedure of Grant-Based Systems is as follows:
· Devices generate data packets to be transmitted.
· Devices send a Preamble on the PRACH to request resources from the BS.
· The BS responds with a Random Access Response (RA response).
· Devices send a "Message 3" to the network, which includes information about the device's capabilities and requirements.
· The network responds with a "Message 4," which includes the resource allocation grant. (Here the Contention Resolution process is used to resolve potential conflicts that may arise when multiple UEs send Preambles on the PRACH simultaneously. This process ensures that each device is assigned a unique set of resources for data transmission and helps minimize interference and collision in the network.)
· Devices send the data packets using the allocated resources on the Physical Uplink Shared Channel (PUSCH).
Grant-Based systems offer efficient resource utilization, reduced latency, and improved throughput for high-data applications. However, they may not be suitable for applications with strict low-latency requirements, as the grant process can introduce delay.
By selecting the most appropriate approach for specific use cases, they can optimize network performance, minimize conflicts and congestion, and provide a high-quality user experience.

