High Throughput Satellites (HTS), are advanced spacecraft designed to provide significantly higher data transmission capacity compared to traditional satellites. HTS satellites can be divided into Geostationary Orbit (GEO) and Non-Geostationary Orbit (NGSO) according to their different orbits. At present, the HTS satellites applied in orbit are mostly GEO.
HTS operate in Ka-band or Ku-band frequencies and offer data rates ranging from tens to hundreds of Gbit/s, immensely surpassing the capabilities of traditional satellites (10 Gbit/s). They support diverse applications like broadband internet, cellular backhaul, government/military communication, and in-flight connectivity. HTS leverage advancements like frequency reuse, multiple spot beams, and higher frequency bands. With these advanced technologies, HTS systems have a lower cost per transmitted bit compared to traditional satellites. This cost efficiency makes them more affordable for operators and users, enabling cost-effective broadband and communication services.
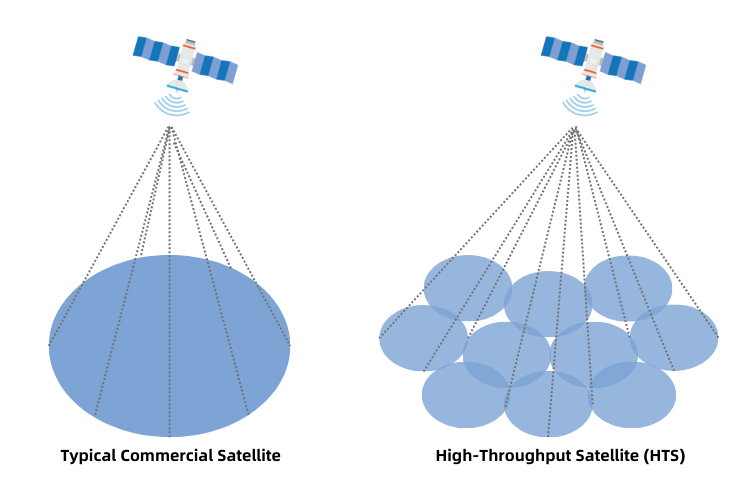
Traditional satellites typically use a single wide-beam to cover a large geographical area, which can lead to limited capacity and poor signal quality. While HTS satellites use multiple narrow spot beams, which allows them to focus their power and bandwidth on smaller, more targeted areas. This improves overall signal quality and capacity, especially in areas with high demand of network services.
· Cost: HTS development and maintenance can be expensive, including satellite construction, launch, and ground infrastructure costs.
· Spectrum Availability: Securing sufficient spectrum for high data rates and capacity can be challenging due to spectrum congestion and regulatory constraints.
· Interference: Coordinating with other satellite systems to avoid interference is crucial, especially in densely populated satellite orbits.
· Ground Infrastructure: Establishing a robust ground infrastructure to support HTS operations, including gateway stations and network management systems, requires significant investment and coordination.

